CASTANHA DE BARU
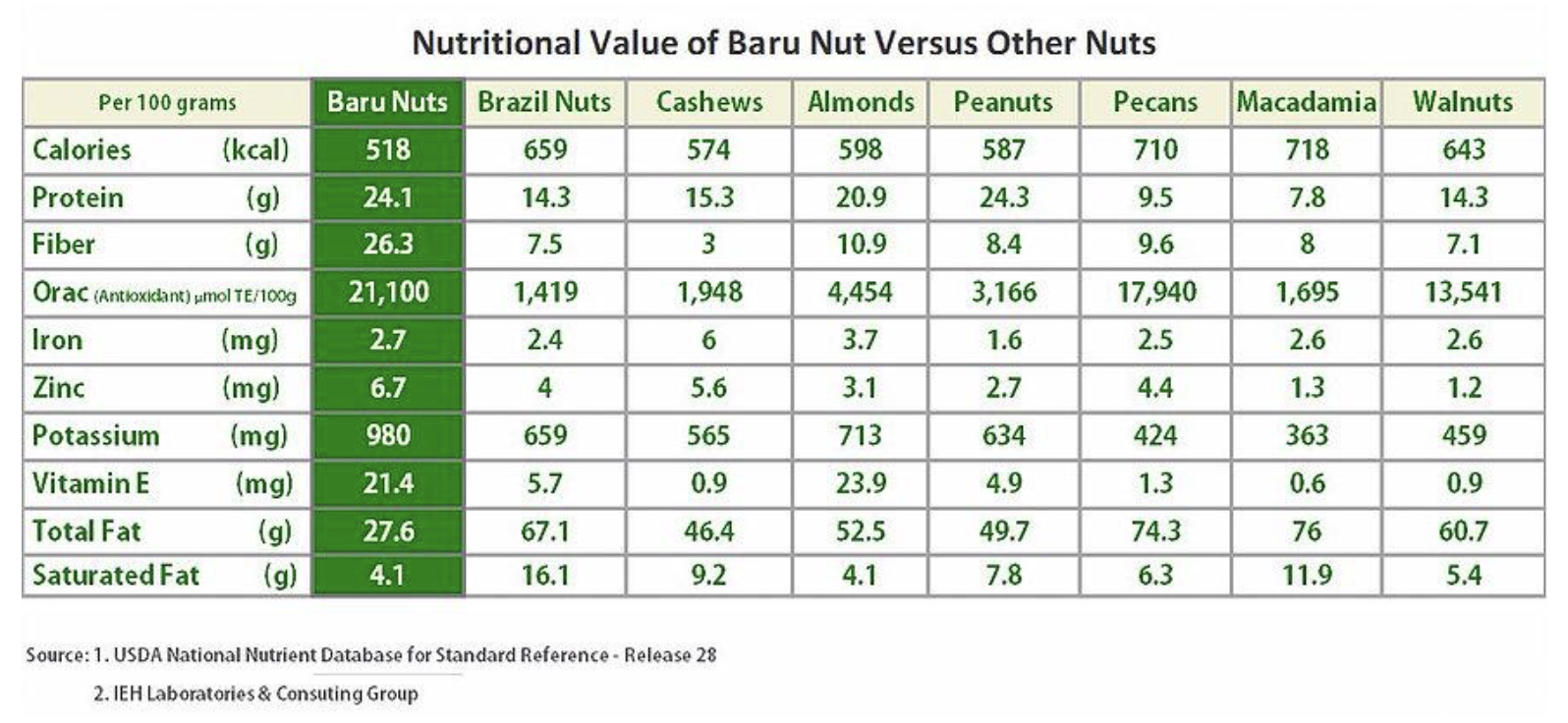
Baru is a fruit from the Brazilian cerrado, known for its rich flavor and high content of protein, fiber, and essential nutrients, making it one of the most nutritious wild foods available.
With the increasing demand for healthy and sustainable food options, its seeds—commonly referred to as "baru nuts"—are gaining popularity due to their impressive nutritional profile. Their demand has been rising significantly both in Brazil and around the world.


[box_title font_size=”15″]SUSTENTABILIDADE[/box_title]
In an environmental context:
- Low water footprint (does not require irrigation, unlike most other crops);
- Regenerative agricultural practices – the baru tree is a deep-rooted carbon sequestrator that acts as a sponge, connecting to the Guarani aquifer—the largest in the world, which supplies São Paulo—and lies beneath the cerrado. *It could participate in carbon offset and trading programs;
- Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions – it requires fewer inputs and does not necessitate deforestation;
- Planting baru trees can help restore areas degraded by traditional monocultures.
